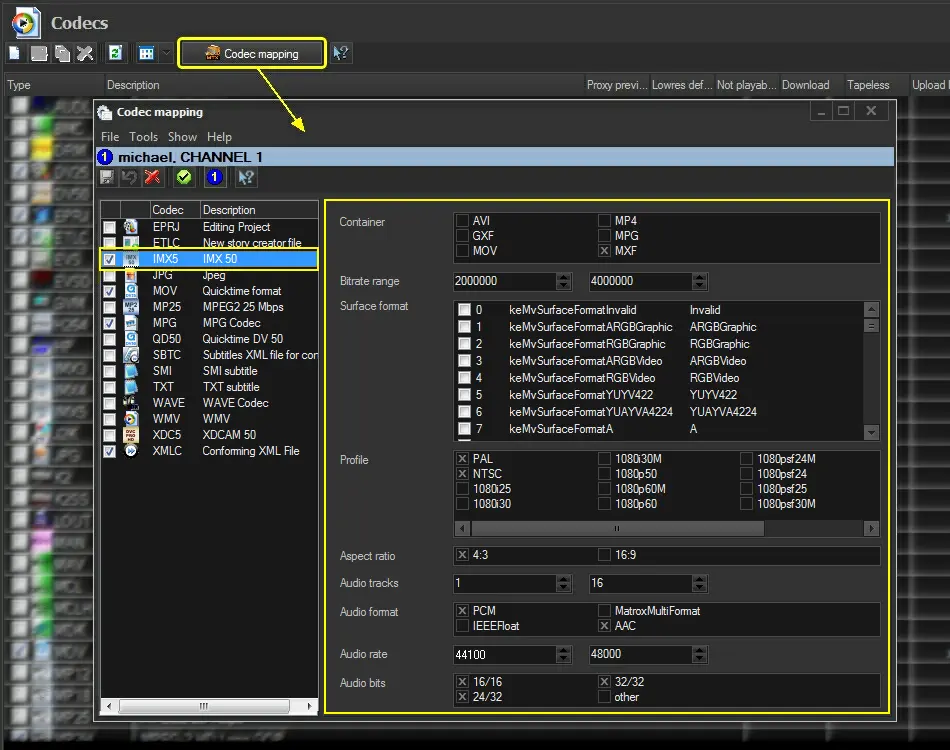
59.2.33.2 Codecs Mapping
The "Codec Mapping" tool allows defining the encoding information of each codec managed by the station.
After launched, the user interface was mainly divided into two areas:
Media_Info_Codec_Mapping
List of codecs (left)
All codecs configured under the Codecs table are displayed:
The codecs with the "tick" are codecs with mapping information (i.e. already configured). All the codecs unticked don't have any mapping information (i.e. not yet configured).
Encoding information (right)
It displays customisable information that identifies a codec.
Fields displayed here are based on Etere's file info metadata (container, bitrate, surface, profile, aspect ratio, etc.).
To define a codec mapping, follow the compilation steps below:
1. In the left panel, select the codec to be mapped
2. In the right panel set the following parameters according to the selected codec:
Container(s): Wrapper containing video stream, audio stream and sundry data. Available values include AVI, GXF, MOV, MP4, MPG, MXF and TS.
Bitrate range: Amount of video data stored in each second of media. The interval can be set from a minimum (0 bps) to a maximum (2'000'000 bps).
Surface format(s): Compression format of motion video data. Available values include: 14 (DV50 422), 27 (Mpeg D10 422), 46 (ProRes), 56 (DNxHD), 0 (invalid), etc.
Profile(s): Video standard of video stream transmission. Available values include: PAL, NTSC, 1080i25, 720p50, unknown, etc.
Aspect ratio(s): Proportion between the width and height of pictures. Available values include: "4:13" and "16:9".
Audio tracks: Specify the number of tracks contained in the audio stream. The interval can be set from a minimum (0 tracks) to a maximum (9999 tracks).
Audio format: Compression format of audio data. Available values include PCM, IEEEFloat, Matrox MultiFormat and AAC.
Audio rate: Sample rate of audio data. The interval can be set from a minimum (0 Hz) to a maximum (48000 Hz).
Audio bits: Bit depth of the audio data. Available values include 16/16, 24/32, 32/32 and others.
3. Press the [save] button to store mapped data in the database (if no conflict is detected).
4. Once a codec is mapped, it will be possible to determine if a file corresponds to that codec (e.g. IMX50) based on its file information, for instance:
Container=MXF
Bitrate=50000
Surface=MPEGD10_422
Profile=PAL
Aspect ratio=4:3
Audio tracks=8
Audio format=PCM
Audio rate= 48000
Audio bits=24/32
Resolve mapping conflicts
The [Conflicts check] button detects conflicts between mappings. A mapping conflict occurs when two codec mappings are considered ambiguous, or all their encoding information coincided partially or totally.
Resolving conflicts is very important since conflicts prevent establishing codecs based on their encoding information (i.e. given certain encoding information, there will be two or more suitable codecs; thus, it is impossible to determine the right codec corresponding to them).
The following example illustrates how conflicts are managed:
•Correct mapping: In the example below, the WMV mapping is correct as at least one encoding information (surface) differs from the IMX50 mapping:
IMX50
Container - MXF, MOV
Bitrate - 2000000 - 4000000
Surface - 19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27
Profile - PAL,NTSC,1080i25
Aspect ratio - 4:3,16:9
Audio tracks - 1-16
Audio format - AAC, PCM
Audio rate - 44100 - 48000
Audio bits - 16/16, 24/32, 32/32
WMV (correct)
Container - AVI
Bitrate - 2500000 - 3500000
Surface - 35
Profile - PAL,NTSC
Aspect ratio - 4:3
Audio tracks - 8
Audio format - PCM
Audio rate - 44800
Audio bits - 32/32
The lack of conflicts will make it possible to determine the codec in the following example:
File information: Container=AVI; Bitrate=3000000; Surface=23; Profile=PAL; Aspect ratio=4:3; Audio tracks=8; Audio format=PCM; Audio rate=44800; Audio bits=32/32
Matching codec: IMX50
•Wrong mapping: In the case below, the WMV mapping is incorrect (ambiguous) since all its encoding information partially coincides with the IMX50 mapping:
IMX50
Container - MXF, MOV
Bitrate - 2000000 - 4000000
Surface - 19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27
Profile - PAL,NTSC,1080i25
Aspect ratio - 4:3, 16:9
Audio tracks - 1-16
Audio format - AAC, PCM
Audio rate - 44100 - 48000
Audio bits - 16/16, 24/32, 32/32
WMV (wrong)
Container - AVI
Bitrate - 2500000 - 3500000
Surface - 23
Profile - PAL, NTSC
Aspect ratio - 4:3
Audio tracks - 8
Audio format - AAC
Audio rate - 48000
Audio bits - 24/24
The conflict will make it impossible to determine the codec in the following example:
File information: Container=AVI; Bitrate=3000000; Surface=23; Profile=PAL; Aspect ratio=4:3; Audio tracks=8; Audio format=ACC; Audio rate=48000; Audio bits=24/24
Matching codec: UNKNOWN (either IMX50 or WMV can be matched)
Using codec mappings
The encoding information of media files linked to assets is stored in Etere's file info metadata (container, bitrate range, surface format and profile). The File info metadata of media files can be used to determine their codec, either manually or automatically:
Manually - Open the "Codec Mapping" form; under the "Tools" menu, choose to apply settings to either "all files with unknown codec" (e.g. ingested via web) or to "all files" (i.e. without any distinction).
Automatically - Launch a T-workflow containing an MTX File Info action for the desired asset. The codec of the asset's linked file will be automatically determined based on its detected encoding information.
NB: Please note that if the file metadata doesn't coincide with any codec mapping, the codec will be set as "unknown".