65.3.3 H265 Encoding
What is H265?
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding(AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4 Part 10).
In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware.
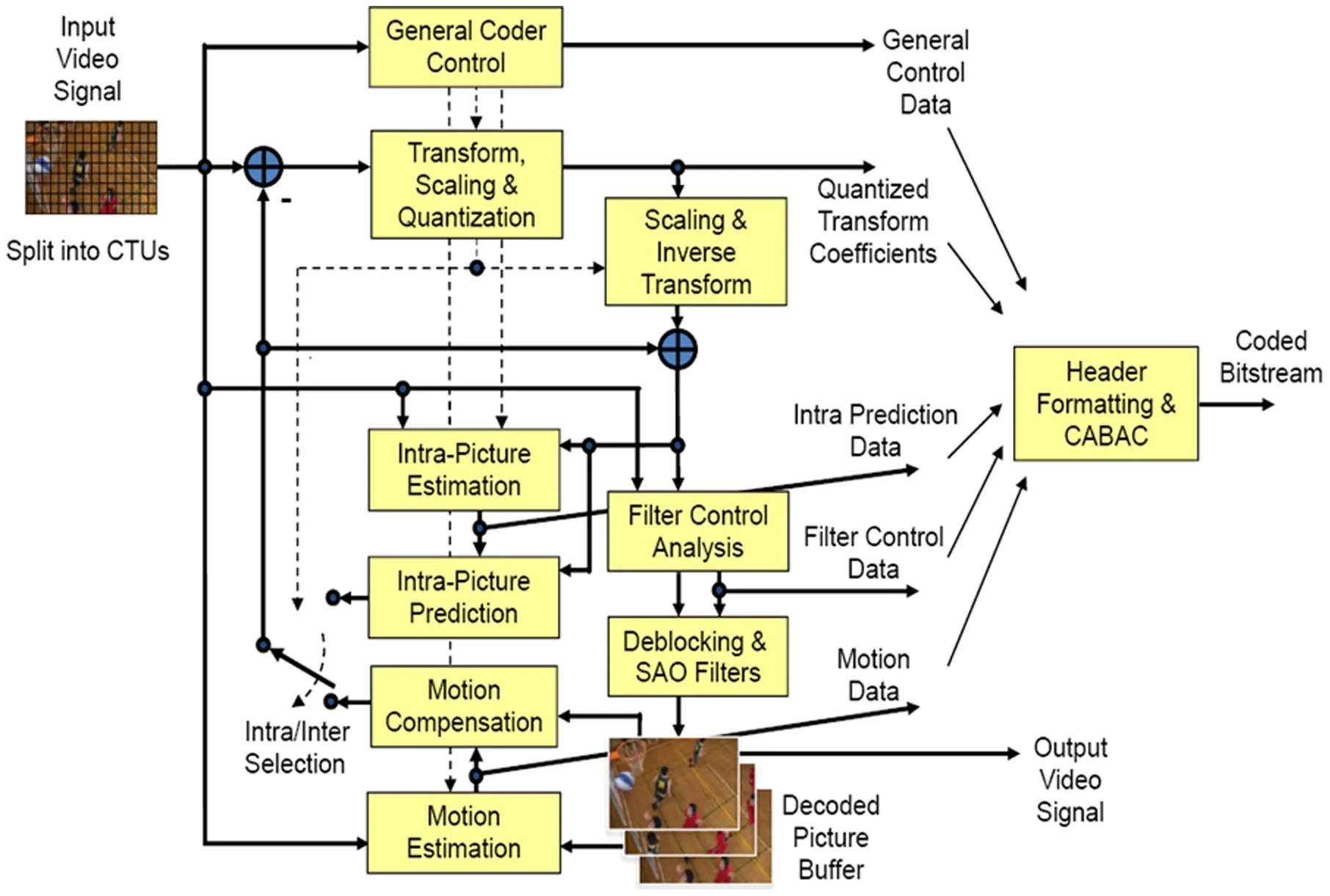
While AVC uses the integer discrete cosine transform (DCT) with 4×4 and 8×8 block sizes, HEVC uses both integer DCT and discrete sine transform (DST) with varied block sizes between 4×4 and 32×32. The High Efficiency Image Format (HEIF) is based on HEVC.
HEVC_Block_Diagram
H264_VS_H265
Codec Overview
The HEVC standard for video compression has the potential to deliver superior performance compared to its predecessors like H.264/AVC. While HEVC shares a similar core structure with AVC and MPEG-2, it incorporates several incremental and much-needed improvements, including:
- Increased flexibility in partitioning;
- Greater flexibility in transforming block sizes and prediction modes;
- Enhanced interpolation and deblocking filters;
- Improved signaling of modes and motion vectors;
- Efficient parallel processing capabilities;
These cumulative advancements have resulted in a video coding format that offers significantly improved compression without compromising quality, even for high-end video content. Here's a brief overview of other important aspects you should know about the H.265 video compression format.
Profile, Levels, and Parameters
A profile represents a set of tools required for coding that are used to create bitstreams specific to that particular profile. An encoder for a specific profile selects the coding tools necessary to generate a relevant bitstream. Conversely, a decoder for a particular profile must support all the encoding tools utilized by the profile.
In technical terms, the initial version of HEVC defined three profiles:
- Main;
- Main 10;
- Main Still Picture.
The second version added 21 range extension profiles, one multi-view profile, and two scalable extensions profiles. This has further undergone a few changes and modifications.
Regarding tiers and levels, the HEVC standard defines two main tiers - High and Main - along with thirteen levels. A level represents a set of constraints for a bitstream. Levels below 4 allow only the main tier. Tiers were developed to accommodate applications with varying maximum bitrates. The Main tier is designed for most applications, while the High tier caters to more demanding high-end applications. A decoder conforming to a given level/tier should easily decode all bitstreams encoded for that level/tier and all lower levels/tiers.
Applications of H.265
The H.265 codec employs a macroblock-encoding method called Coding Tree Units (CTU), which differs from H.264. CTU enables higher coding efficiency and supports 64x64 macroblocks. This makes the H.265 format highly useful in various applications, including:
- H.265 supports a wide gamut of color spaces - such as NTSC, Rec. 601, PAL, generic film, SMPTE 170M, sRGN, sYCC, and more;
- Seamless video streaming and data sharing for next-generation HDTV displays and content capture systems.
Why H.265 compression?
The simple answer to this question is improved efficiency. The efficiency of a codec increases when it can compress and decompress an image using fewer bitstreams without sacrificing quality. From this perspective, H.265 is significantly more efficient than the H.264 codec. Furthermore, with evolving viewing resolutions and the proliferation of high-resolution screens, it makes sense to adopt a compression technique designed for modern video requirements.
Benefits of H.265
To summarize, here are the key benefits and improvements offered by the H.265 compression standard:
- Provides double the compression ratio of H.264;
- Supports 64x64 pixel macroblocks, as compared to the 16x16 that was supported by H.264;
- Enhances video compression through improved motion prediction mechanisms;
- Offers more detailed interframe predictions compared to H.264;
- H.265 supports resolutions much higher than 8K Ultra High-Definition which is supported by H.264;
- H.265 works on much fewer bit rates as compared to H.264 codecs, thereby making the entire process a lot more efficient.