70.1.2 Archive Exchange Format (AXF)
Archive Exchange Format (AXF) is an open format that supports interoperability among disparate content storage systems. AXF is a file system within a file that can store any type of data on any storage media. As AXF itself contains the file system, it can exist on any generation of data cartridge, tape, spinning disk, optical disk, flash drive, etc.
AXF includes a self-describing characteristics at the object level and media level, all media and objects can be fully indexed and recognized by any system that comprehends AXF.
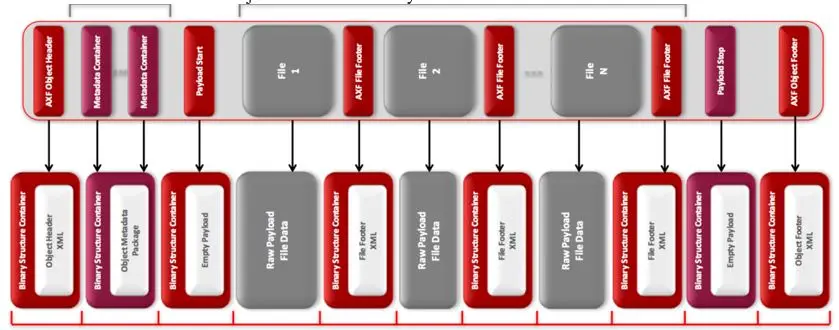
AXF object comprised of four main components:
•AXF Object Header
A structure containing descriptive XML metadata such as AXF object’s unique identifier (UUID and UMID), creation date, object provenance, and file-tree information including file permissions, path, etc.
•AXF Generic Metadata packages
The AXF Generic Metadata packages are self-contained, open metadata containers in which applications can include AXF object-specific metadata. This metadata can be structured or unstructured, open or vendor-specific, binary, or XML. There is no constraints or standard governing the type of metadata, the number of packages and their contents. If there is no metadata to store along with the AXF object, this structure is simply omitted.
•AXF File Payload
It is the actual byte data of the files encapsulated in the objects. The payload consists of any number of triplets – file data, file padding, file footer. File padding ensures alignment of all AXF Object elements on storage medium block boundaries, it is key to the AXF specification. The File Footer structure contains the exact size of the preceding file, along with file-level checksum designed to be processed on-the-fly by the application during restore operations with little or no overhead. These file footers add to the enhanced resiliency of AXF as they can be used to recover file payload data even if the AXF Object Header and Footer structures are missing or corrupt.
•AXF File Object Footer
The AXF Object Footer contains the information of AXF Object Header plus information captured during the AXF object’s creation, checksums, precise file size and structure block positions. The AXF Object Footer is important to the resiliency of the AXF specification because it allows efficient re-indexing by foreign systems when the media content is not previously known, offering media transport between systems that follow the AXF specification.
HSM axf file structure diagram
Consistency Check
When processing AXF file format, HSM Data Pump would perform a consistency check on data format before writing to database. The consistency check results would be written into log file for assessment. The consistency check includes:
•Start and End data block
•Data position on tape
•The congruent in file size
List below are some example of possible errors resulted from the consistency check:
! Consistency check! Archive was not performed: checked inhiblock = 0, endblock = 0, remaining = 0
! Consistency check! Archive was not performed: checked inhiblock before = 66079, after = 66079
! Consistency check! Not enough written blocks: expected = 6707, written = 0
NB: When performing AXF archive, HSM DataPump would update the physical end-of-tape to database and resume AXF archive on another tape.