59.8.3.9 SNMP Parameters
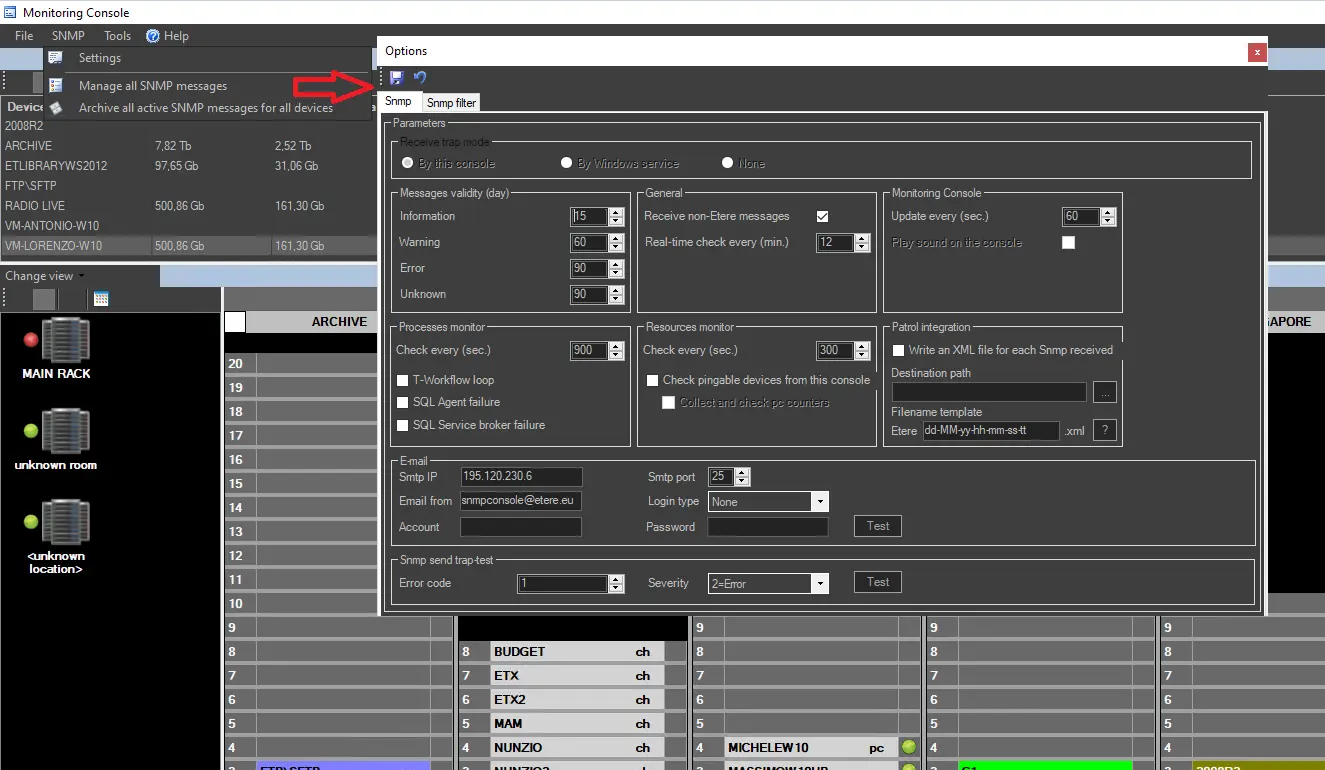
The main options of the Monitoring Console can be accessed through the Etere Configuration > Monitoring Console > SNMP menu; there, it will be possible to specify the following parameters:
Monitoring_Console
Receive trap mode
The currently used mode, previously set on the connection parameters, will be displayed.
Messages validity
Specify the maximum number of days that Information", "Warning", "Error", and "Unknown" messages will be kept in the database (before being definitively deleted).
General
Set the following parameters regarding monitoring checks.
• Receive non-Etere messages: If enabled, SNMP messages generated by other systems (e.g. from routers, video servers, etc.) different than Etere will also be allowed.
• Real-time check every: Set the frequency with which the console will check that Etere modules are correctly running in the computers where they are installed.
NB: Use the "resources monitor" option for device-specific real-time monitoring.
Monitoring Console
This section configures the console to respond to the SNMP messages.
• Update every (sec.): Set an interval (in seconds) to update the Monitoring Console.
• Play sound on the console: If enabled, the sound effects will be triggered when the SNMP message arrives at the Monitoring Console.
Processes monitor
Set here the interval (in seconds) for monitoring and sending SNMP messages from the following processes:
• T-Workflow loop
• SQL Agent failure
• SQL Service broker failure
Resources monitor
You can define how the resources would be managed.
• Check every: Set the interval for checking the resource status.
• Check pingable devices from this console: If enabled, the current console will monitor -every "n" seconds- all the devices whose pingable property is true. Moreover, if the "auto-refresh" option is enabled on the Resource Viewer, an SNMP error (25000) will be displayed for all devices with missed pings. The status of this function will be displayed in the monitoring status bar of the Monitoring Console.
The auto-ping counter indicated above will be reset when you close and reopen the Monitoring Console. Alternatively, you can issue a manual ping command to a device using the “Ping device” function in the Toolbar menu.
It's worth mentioning that by default, all devices are enabled to be pinged and raise an SNMP error in case they don't respond. For more details on device properties, please look at Resource Properties.
NB: Ping errors are directly stored in the SNMP database following filtering rules but without sending them to the Monitoring Console; this allows Etere to record the device's IP address (otherwise, it will record the IP address of the Monitoring Console, which sent the message). Additionally, all pings are logged into the config.Res.MonitoringConsole.log file within the Etere logs folder, indicating their success or failure.
• Collect and check PC counters: If enabled, the System Information service will be enabled in the current console, thus allowing it to monitor the counters of all the Etere PCs. This function will be available in the monitoring status bar of the Monitoring Console.
NB: This function is available only if the "check pingable devices from this console" is enabled.
Patrol integration
You'll be able to define the action to be taken while patrolling the Monitoring Console.
• Write an XML file for each SNMP received: If this option is enabled, an XML file will be created in the designated path when any SNMP message arrives at the Monitoring Console.
• Destination path: Indicate the directory path to store the XML files generated from the Monitoring Console. You can click the browse button to locate the path.
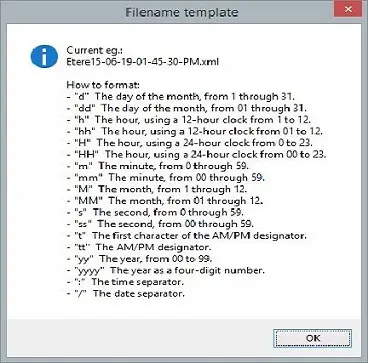
• Filename template: The XML file would be created with prefixes “Etere” and “dd-MM-yy-hh-mm-ss-tt” to indicate the date and time of the file creation. The template can be customised.
You can click on the question mark button to view the filename template.
Filename_template
E-mail
Here, all the relative information regarding how reports are sent through the SMTP mail transfer protocol can be defined; there's also a test button to check if the data is correct.
• SMTP IP: Enter the IP address of the mail server where the mail account used to send notifications is configured.
• SMTP port: The communication port of the mail server.
• Email from: The email address that will send the email notifications when the SNMP console receives messages. The recipient's email address can be configured in the SNMP filters, as explained in the next chapter.
• Login type: Choose if the login is required or not.
• Account and Password: Enter the credentials of the mail account used to send notifications.
The following example explains how to use a Google account and set it as SSL.
This example regards only Google accounts, and to work, you'll need two steps of authentication inside your Google account:
1 - Login to your Google account, go to "Security > two steps authentication", and enable it.
2 - Return to your Google account under "Security" and click "app passwords" Generate an app password and memorise it (essential; otherwise, you'll need to generate another).
After those two steps, you'll be able to use this modification by checking "Enable SSL" and using the password generated from your Google account (not the usual login password of Gmail)
Once these changes have been made on the Google side, return to ETERE and enter the above parameters.
NB: the port to use is 587 and not 465.
SNMP send trap test
Here, you can test the SNMP sending service by sending a text message with a custom error code and a certain severity.
NB: From Etere version 33.2.171.6688, sending messages with hexadecimal codes more significant than the value 32000 (dec) is possible.