65.3.2 H264 Encoding
What is H264 and H264 Encoding
- H264 encoding is one of the most commonly used formats for recording, compressing, and distributing video content. It is known to produce good video quality at a substantially lower number of bits processed per unit of time compared to previous standards.
- H264 is a codec or video compression technology jointly developed by ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) and the ISO/IEC JTC1 Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG).
ITU-T's H264 standard and the ISO/IEC MPEG-4 AVC standard are jointly maintained to have identical technical content, and the terms are interchangeable.5479_etx_writer_h264_enc
Popular Uses of H264 Encoding
- One of the video encoding standards for Blu-ray Discs.
- Streaming internet sources, such as videos from Vimeo, YouTube, and iTunes Store
- Web software such as Adobe Flash Player and Microsoft Silverlight
- HDTV broadcasts over terrestrial (Advanced Television Systems Committee standards)
- ISDB-T
- DVB-T
- DVB-T2
- Cable (DVB-C)
- Satellite (DVB-S and DVB-S2)
- File Formats:
H264 can be integrated into multiple file formats containing various types of compressed data. It is frequently produced in MPEG-4, which uses the .MP4 extension, as well as QuickTime (.MOV), Flash (.F4V), 3GP for mobile phones (.3GP), and the MPEG transport stream (.ts). H264 video is also commonly encoded with audio compressed with the AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) codec, an ISO/IEC standard (MPEG4 Part 3). - Nvidia NVENC H264 encoder
Nvidia NVENC was introduced with the Kepler-based GeForce 600 series as a product feature that offloads H264 video encoding from the host CPU.The NVIDIA Encoder (NVENC) provides high-quality video encoding faster and more power efficient than CUDA-based or CPU-based encoders. The CUDA cores and system CPU can run other compute-intensive tasks when using dedicated hardware for video encoding and decoding.
- Using NVENC
NVENC support is available in ETX free of charge.
According to NVENC specs, GeForce cards are limited to 2 streams and Quadro to 6 streams.
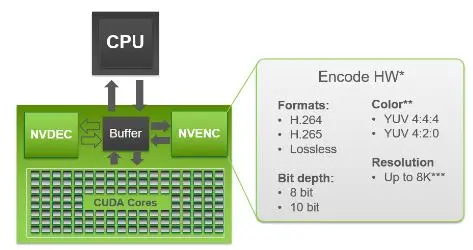
NVENC encoder's ID is "n264".The hardware supported by NVENC encoding is indicated in the diagram below:
Nvidia video encoding hwNB: The NVENC encoder requires a monitor/dongle to be plugged in as the main monitor and uses all NVENC sessions during encoding. Without the monitor/dongle, metadata would not be written.
- Performance
NVIDIA's latest generation of Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) based on the Kepler and Maxwell architecture contain a hardware-based H264 video encoder. It is commonly referred to as NVENC.NVENC, dedicated to H264 hardware on the GPU chip, does not use the GPU's graphics engine and hence uses much less overall system power than the older CUDA-based encoder.
It also leaves the CPU and GPU graphics engine to perform other tasks. The hardware is optimized to provide excellent quality at high performance, enabling a wide range of applications that require video encoding capabilities.
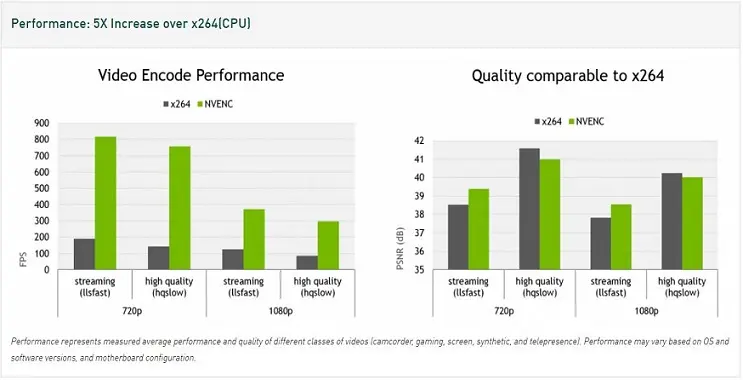
The diagram below provides video encoding performance by NVENC on different resolutions.
Nvidia video encoding performanceNote: The above performance measured the average performance and quality of different classes of videos (camcorder, gaming, screen, synthetic, and telepresence). The performance may vary based on operating systems, software versions, and system-board configuration.
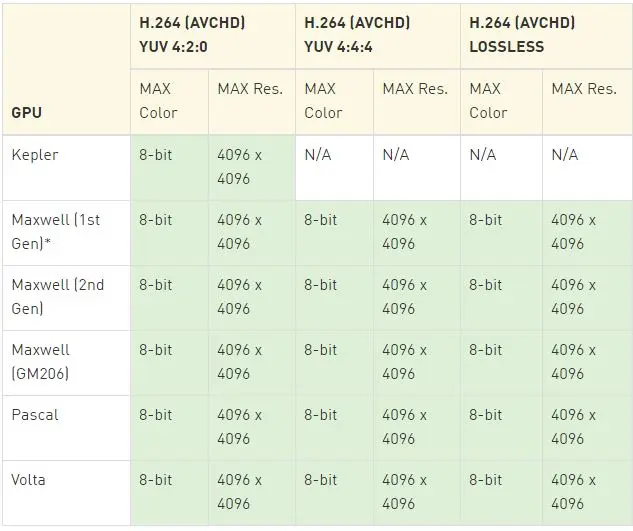
A comparison between different image formats is listed below:
Nvidia video encoding compared - Nvidia CUDA Encoder
The Nvidia CUDA encoder works with Nvidia cards that support CUDA and uses both the CPU and GPU during encoding. - Using Nvidia CUDA
Starting from the 340.52 drivers, CUDA encoding has been disabled. A previous version of Nvidia drivers is needed (for example, 337.88). - Performance
It has a much higher GPU usage than NVENC and produces no dropped or skipped frames while encoding. However, NVENC produces high quality compared to Nvidia CUDA. - Intel Quick Sync
Intel Quick Sync has the advantage of speed and efficiency. Speed is prioritized over quality. Video content is typically compressed and encoded into a specific format when stored. When you want to use that content, it must first be decoded and then re-encoded in a new format, resulting in a resource and time-intensive process.
Intel Quick Sync Video uses the dedicated media processing capabilities of Intel® Graphics Technology to decode and encode at high-speed capabilities. - Using Intel Quick Sync
Based on Intel Media SDK, two modes are available: software (CPU-based) and hardware-accelerated (GPU-powered). - Performance
GPU version provides significant quality (using the hardware codec available on the Intel processors). It does not use the CPU, thus freeing up the CPU's usage. This results in fast speeds with no dropped or skipped frames during encoding. The GRU is the recommended version as it produces much better quality.The Central Processing Unit (CPU) version uses much of the overall system power, resulting in many breaks and buffer overflow while recording and the occurrences of corrupted files.
x264 Encoder (GPL)
x264 is a free software library and application for encoding video streams into the H264/MPEG-4 AVC compression format and is released under the terms of the GNU GPL.
X264 encoder supports features necessary for many applications, such as television broadcasts, Blu-ray low-latency video applications, and web video. This format forms the core of many web video services, such as YouTube, Facebook, Vimeo, and Hulu. Television broadcasters and ISPs widely use it. - Using x264
Two presets are available: the "faster" and the "superfast preset". GPL license prohibits using this encoder in commercial applications without a special license. x264 is available under a commercial license from x264 LLC and CoreCodec. - Performance
The "Faster" preset relies heavily on CPU usage, resulting in vast breaks and buffer overflow while recording and corruption on file.
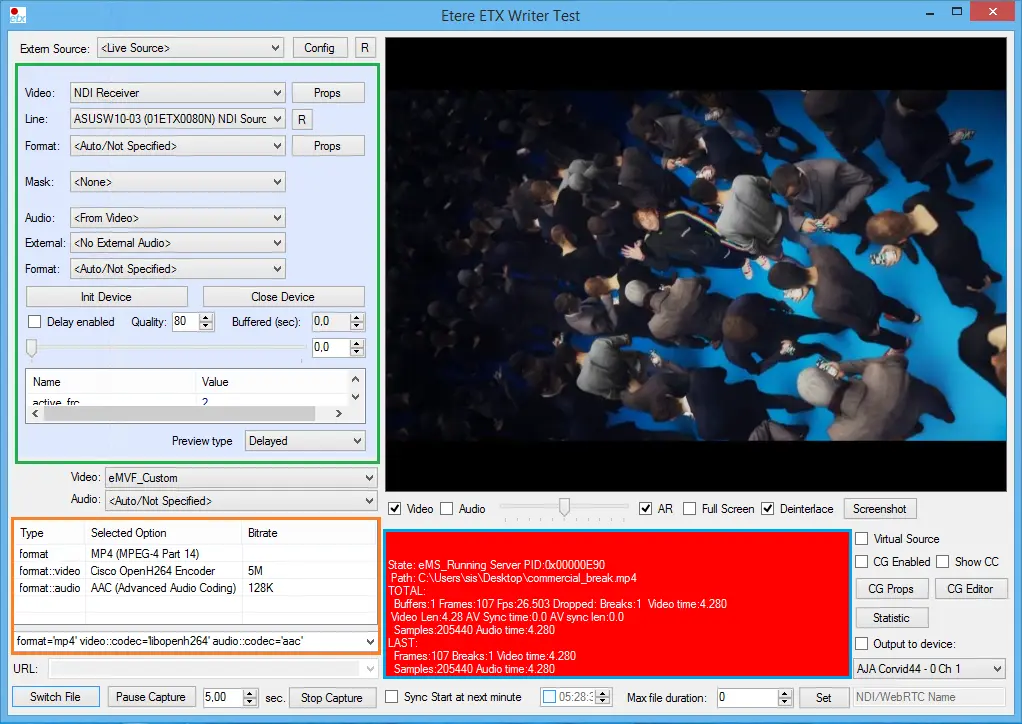
The "Superfast" preset runs on almost half the CPU usage compared to the "Faster" preset, resulting in no dropped or skipped frames while recording. - Testing H264 Encoding
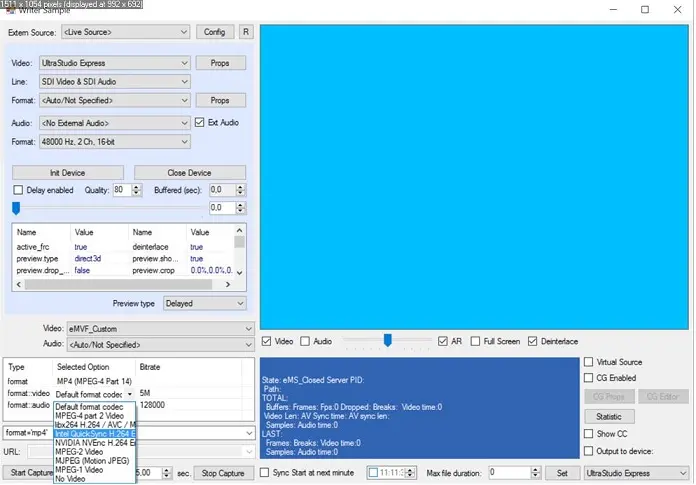
To test the H264 Encoder, you should use a supported processor and graphics card. For example, to use Intel Quick Sync, check that an Intel-based processor supports Intel QuickSync technology and Intel HD Graphics as the default graphics card on your machine. Next, open the ETERE Toolbox Writer application. Select, for example, MP4 as encoding format and open a list of available video codecs. Select an H264-supported encoder for, e.g., Intel QuickSync encoding, and start capturing your video onto the file. Intel QuickSync