1.3.4.5 Database Mirroring
Database mirroring is a solution that increases the availability of SQL Server database; it is implemented on a per-database basis and works only with databases that use the Full Recovery model.
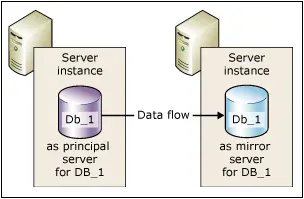
Database Mirroring maintains two copies of a single database; they must reside in different Server instances of SQL Server Database Engine and other locations. Database mirroring initiates a relationship known as a “database mirroring session” between the Server instances. One Server instance would serve the role of Principal Server, while the other Server instance would be a “hot” or “warm” standby “Mirror Server”. The Mirror Server provide “read-only” access to database users.
When a “database mirroring session” is synchronized, the failover to the hot standby Server occurs without data loss. If the session is not synchronized, data may be lost when it failover to a warm standby Server.
Database Mirroring works by redoing every insert, update and delete operation in the central server database onto the mirror server database as quickly as possible by sending a compassed stream of active transaction log records to the mirror server. Unlike database replication, which works on a logical level, database mirroring works at the level of the physical log record.
Operation Modes
Database mirroring session runs in either synchronous or asynchronous operation mode.
•Synchronous operation: Transaction is committed on both databases, which increases the transaction latency.
Synchronous operation use “high-safety-mode” for data transaction. When the session starts, the mirror server synchronises the mirror database with the central database as quickly as possible and commits the transaction on both databases as soon as data are synchronized.
NB: High-safety mode with automatic failover requires a third server known as “Witness Server”. The witness server does not serve the database; it simply supports automatic failover by verifying if the principal server is up and functioning. The mirror server would initiate automatic failover only if the mirror and witness servers remain connected.
•Asynchronous operation: It maximizes the performance by committing transactions without waiting for the mirror server to write the log to disk.
Asynchronous operation use “high-performance-mode” for data transactions. As soon as the principal server sends a log record to the mirror server, it confirms the database user without waiting for the mirror server to commit and write the log to disk.
Database Failover Mode
1. Automatic Failover
This failover mode requires a high-safety manner and the presence of a mirror server and witness server. Before initiation, the database must already be synchronized, and the witness server must be connected to the mirror server for the mirror server to initiate the failover.
2. Manual Failover
This failover mode requires a high-safety mode, both databases must be connected, and the database must already be synchronized.
3. Forces Service
With “high-safety-mode” and “high-performance-mode” without automatic failover, failover is possible if the principal server fails and the mirror server is available to resume the central server role.
The Benefits of Database Mirroring
1. Increases database availability
In the event of a disaster, in “high-safety mode” with automatic failover, the failover can be accomplished quickly without data loss.
2. Increase data integrity
Database mirroring provides complete data redundancy in the database with the “high-safety-mode” or “high-performance-mode” operation. When the mirror server cannot read a page, it automatically requests a fresh copy of data from the principal server.
3. Minimize downtime during server upgrades
With database mirroring, you can sequentially upgrade the instances of SQL Server hosting the failover database, ensuring that the Production database is always available for user access.