1.3.4.6 SQL Cluster
Microsoft SQL Server Cluster is a collection of two or more Microsoft SQL Servers with identical configurations and access to shared storage. It provides the resources required to store the database files.
The SQL Servers in the cluster are referred to as "nodes". Each node communicates with each other via a private network, sending a heartbeat signal between nodes to ensure they are up and functioning. Should one node fails to convey the heartbeat signal, the secondary node would automatically resume ownership of the failed node and continue to provide access to the user's requests.
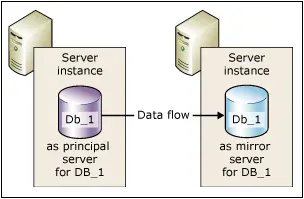
Unlike other clustering technologies focusing on better performance, SQL Clusters are designed to provide high-availability databases to eliminate downtime during hardware failures. In the diagram above, all nodes in the cluster are accessing the same resources stored in shared storage; each node would be mapped to a logical drive which is physically hosted on the shared repository with its associated IP Address and network name.
Microsoft Windows Server 2003 and Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Enterprise Edition allows up to 8 nodes to be combined into a single cluster. For Microsoft Windows Server 2008 and Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Enterprise Edition, you can double the number of nodes to 16.
SQL Cluster failover can be performed manually or automatically. An automatic failover occurs when a node stops sending a heartbeat to other nodes. In contrast, manual failover is more beneficial if patching or other maintenance tasks are required on a physical Server.
SQL Cluster Mode
SQL Cluster came with two modes:
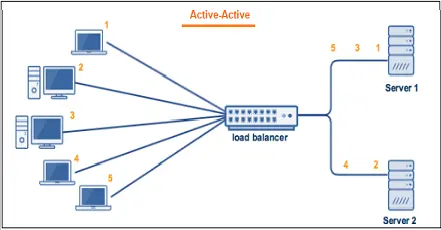
•Active –Active cluster
The active-Active cluster comprises at least two nodes actively running similar services simultaneously. If load balancing is in place, the workloads are distributed across all nodes to prevent overload on a single node. The nodes' configuration is identical in high-availability databases to achieve seamless operations and redundancy.
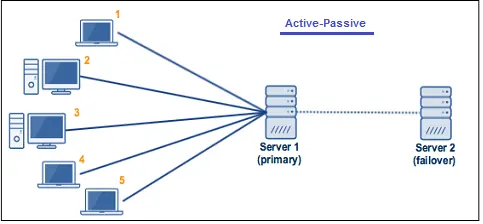
•Active-Passive cluster
Active-Passive cluster made up of at least two nodes as well. However, only one node is active to serve the clients; the other node is in passive or standby mode and only switches to active mode when the primary Server is disconnected. In the event of a failover, the changes made to the primary Server must be cascaded to the failover server to resume operations.
Summary
SQL Cluster protects the database from hardware failure relating to Server hosting the SQL Server instance. Still, unlike Replication, Database Mirroring or Log Shipping, there is no protection against data loss due to media failure without incorporating the redundancy of database storage or database mirroring.
SQL Cluster is an expensive solution that you need to consider. For example, in Active-Passive mode, you need to purchase additional hardware and licenses for a standby server that you hope you will never want to use it.